Integrating Satori with your commits using our Github App
Each time you push code to your GitHub repository, there is a potential risk that may be introduced. To safeguard your project and its sensitive data, it's crucial to minimize the malfunctions or vulnerabilities. The three primary areas of concern are:
- Code malfunction: If you cannot assert how your software behaves, deployment should be considered or stopped.
- Secrets in your code: Hard-coded credentials, API keys, and sensitive data can be unintentionally pushed, compromising the security of your systems.
- Vulnerable code (internal or third-party): Code may contain security weaknesses that malicious actors can exploit.
To automatically safeguard your GitHub repositories and ensure continuous testing, install our Satori App:
1. Install the Satori CI GitHub App:
Go to the Satori GitHub App page. Make sure you are authenticated with GitHub to proceed with the installation. You need to be authenticated to configure it.
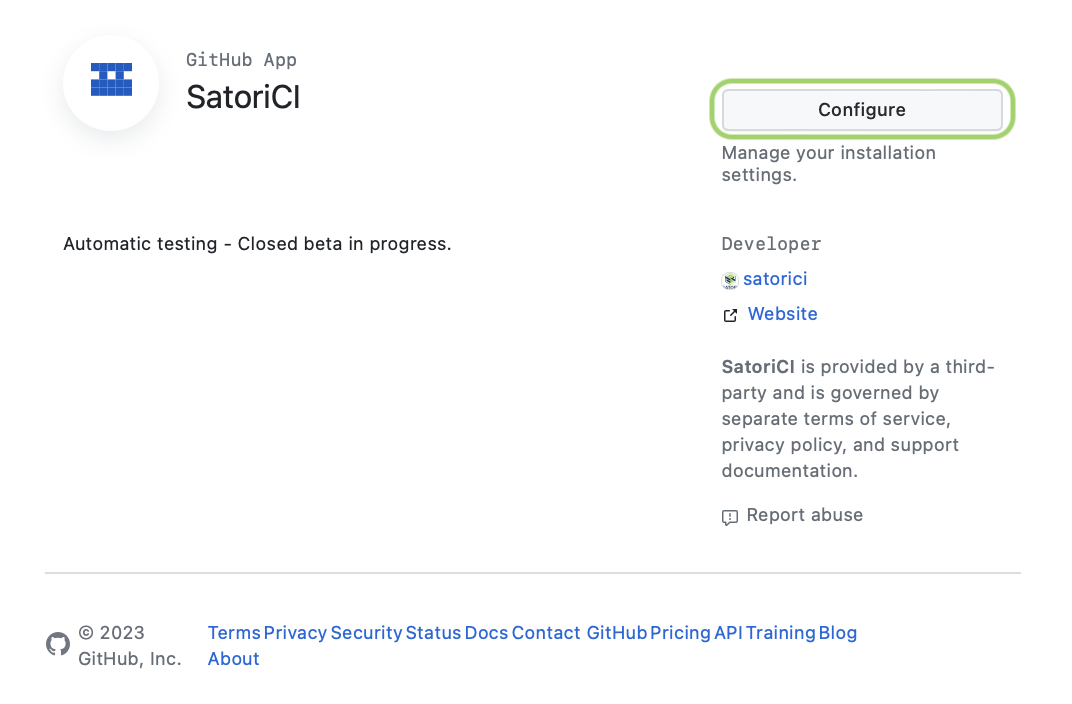
2. Click on Configure:
Select which accounts you will be setting it up for.
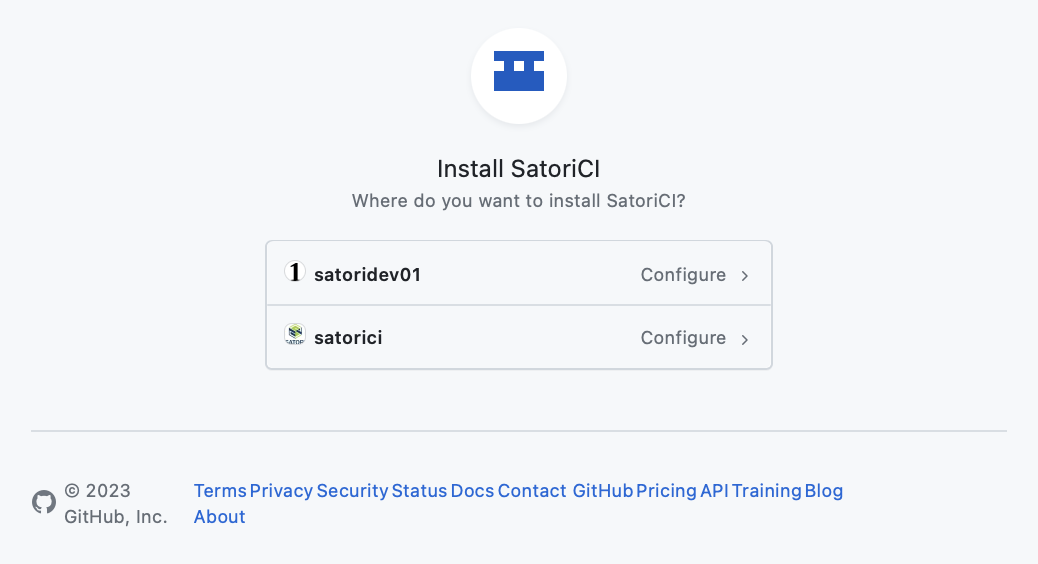
3. Choose the GitHub accounts where you want to set up the Satori CI App:
Select the repositories where you want to install the app. You can choose specific repositories or select All repositories.
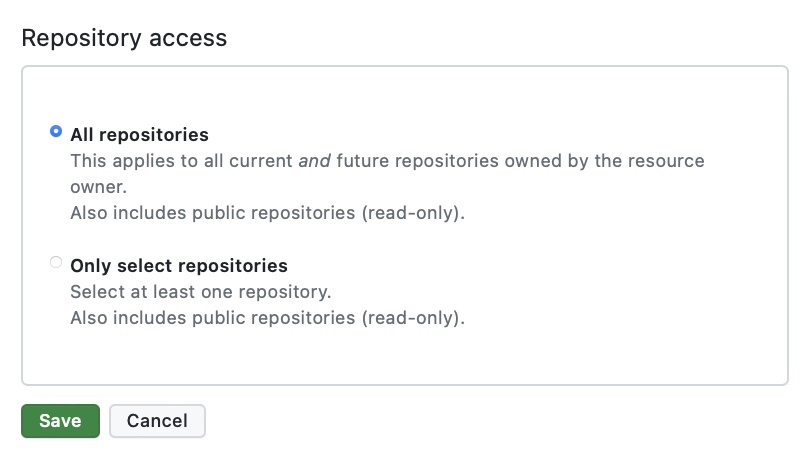
4. Save:
Once you are done, click on Save. We care about your security, so we will only store your email, your repositories names, and the reports. Your code only lives within the virtual machines that are present during the execution.
5. Create your first .satori.yml file:
To begin automating tests in your connected repositories, you need to create a file named .satori.yml. This file will define the tests that will automatically run every time you push new code to your repository. Let's start by keeping it simple and checking for secrets using Trufflehog, a tool that scans for sensitive information such as API keys or credentials that may be unintentionally exposed in your code.
settings:
name: CI Tests for every push of my Repo
import:
- "satori://code/trufflehog.yml"
tests:
assertReturnCode: 0
build:
- make
run:
assertStdoutContains: "An expected output" # assert the output of the main system execution of your project
your_project:
- ./your_projectWith this configuration and the .satori.yml file within your project, automated tests defined in your playbook will be triggered each time you push code to your GitHub repository. These tests will run on every pipeline execution, ensuring continuous validation of your code.
