Run
Satori can be executed in two environments:
- Remotely: run Satori on our cloud platform, which allows for scalable and centralized testing without the need for local resources.
- Locally: execute Satori on your local machine, providing flexibility for development and testing in a controlled environment.
Run Remotely
This playbook named hello.yml remotely using Satori. This playbook is defined as follows:
test:
assertStdoutEqual: "Hello world\n"
assertReturnCode: 0
execute:
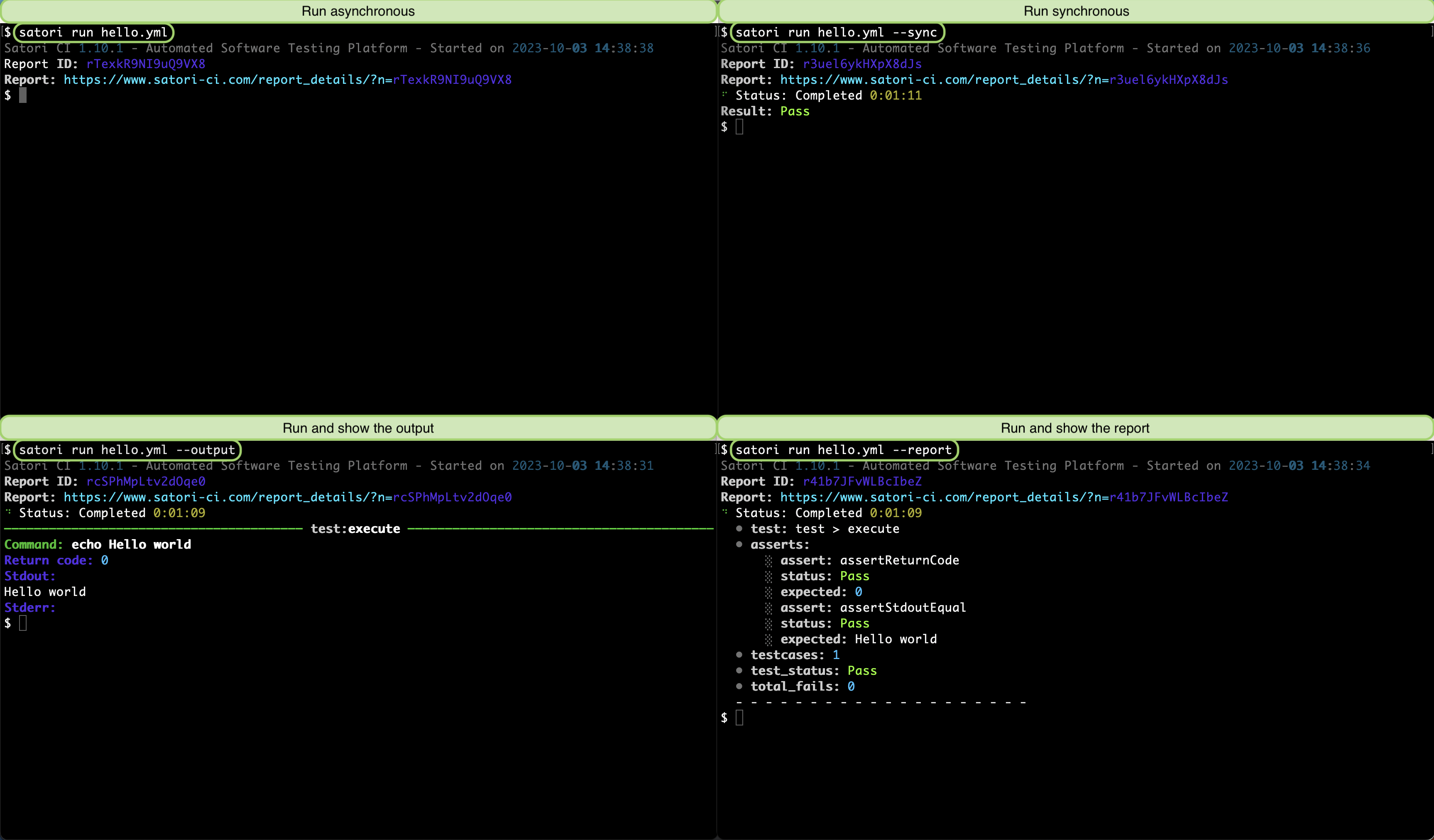
- echo Hello worldWhen executing this playbook, you have several options:
- Asynchronously (no parameters): run the playbook without any additional parameters.
- Synchronously with --sync: execute the playbook synchronously, displaying the status upon completion.
- Synchronously with --report: run the playbook synchronously and generate a report that summarizes the results when it finishes.
- Synchronously with --output: execute the playbook synchronously, showing the output in real-time as it completes.
Run Remotely with Parameters
When creating playbooks in Satori, you can include parameters that need to be defined at runtime. If you use a $ symbol in your playbook for a parameter that is not explicitly defined within the playbook, it will be treated as a required parameter when the playbook is executed.
For example, consider the following playbook named satori://test.yml, which echoes the parameter $:
test:
assertStdoutContains: Hello World
hello:
- echo Hello World
whatever:
- echo ${{WHAT}}To execute this playbook and provide the required parameter, you would run the command:
satori run params.yml -d WHAT="Hello World" --output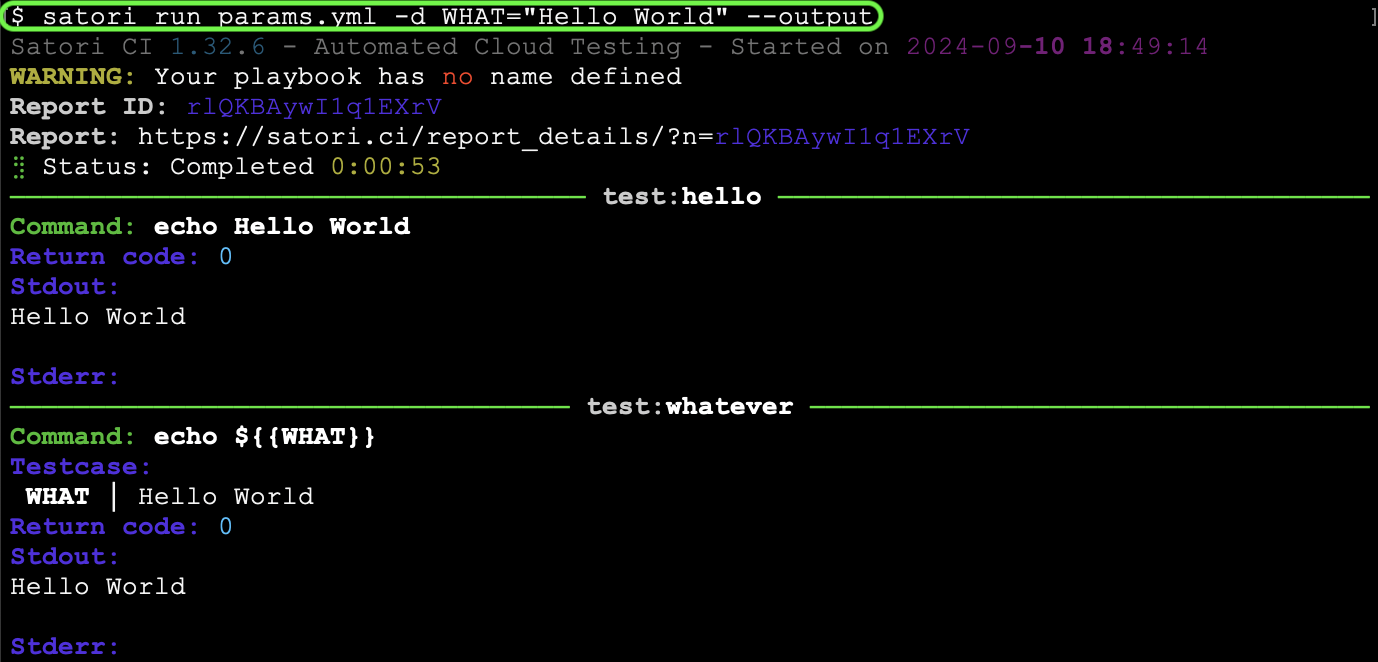
Local testing with Satori Playbooks
When working locally on a directory containing source code, you can save your playbook as .satori.yml within the directory. This approach is similar to how you would structure your repository when testing code through a CI pipeline.
Consider the following example files: main.c, a corresponding Makefile, and a playbook that verifies the expected behavior of your code.
- main.c:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}- Makefile:
all: hello
hello: main.c
gcc -o hello main.c- .satori.yml:
install:
updates:
- apt update >> /dev/null
dependencies:
- apt install -qy make gcc >> /dev/null
tests:
assertReturnCode: 0
build:
- make
run:
assertStdoutContains: "Hello World"
hello:
- ./hello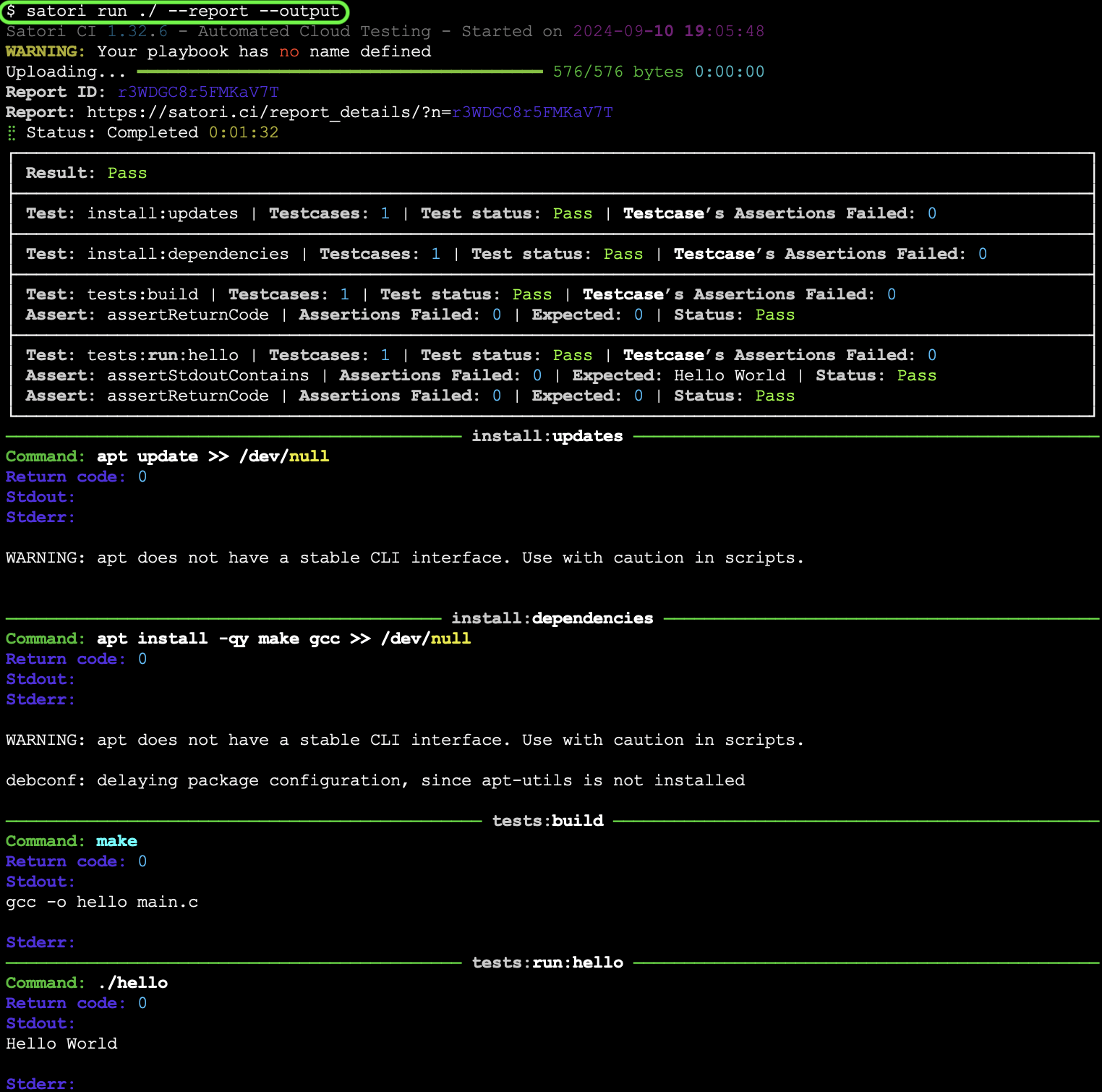
This same playbook can also be employed in CI/CD environments.
Run a public Playbook
You can execute on-demand public playbooks available in the Satori platform. You can see a list of the publicly available playbooks with:
satori playbooks --publicTo run a public playbook, you can execute them passing parameters if required with -d:
satori run satori://some/playbook.yml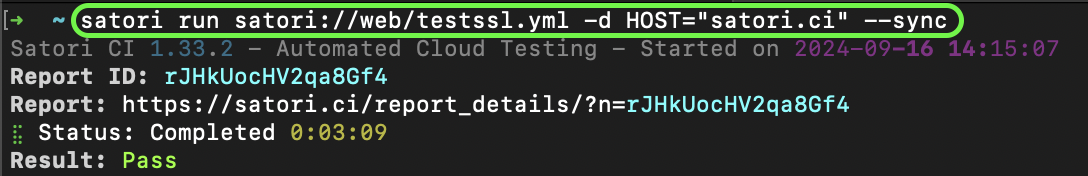
This allows you to leverage existing public playbooks that may already address your specific testing needs effectively.
Run Locally
You can execute the playbook named hello.yml locally, just as you would run it remotely. This allows you to verify that your playbook functions correctly in your local environment, and Satori will confirm the assertion results. Here’s how you can run it locally:
satori local hello.yml --sync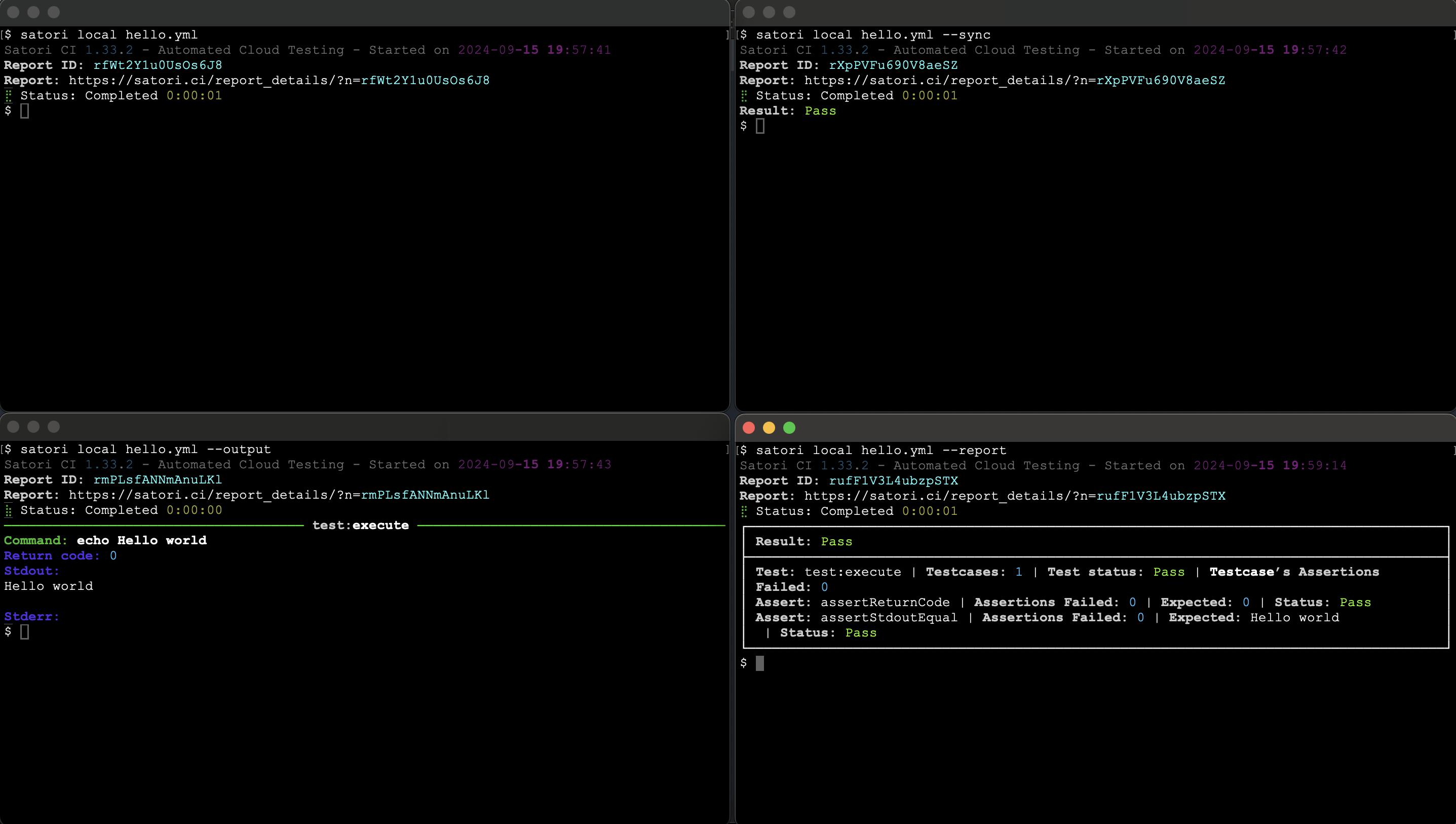
Run a process in Background
When running a service that needs to listen in the background, it's important to ensure that processes do not remain in the foreground, especially when using shell scripting techniques. The recommended approach is to utilize screen, which allows you to run processes in a detached session. Additionally, setting a timeout for the container helps manage its lifecycle effectively. For example:
settings:
name: Background process
timeout: 60
install:
- apt update >> /dev/null
- apt install -qy screen >> /dev/null
background:
- screen -dm sleep 10
check:
assertStdoutContains: "10"
ps:
- ps wuax | grep sleep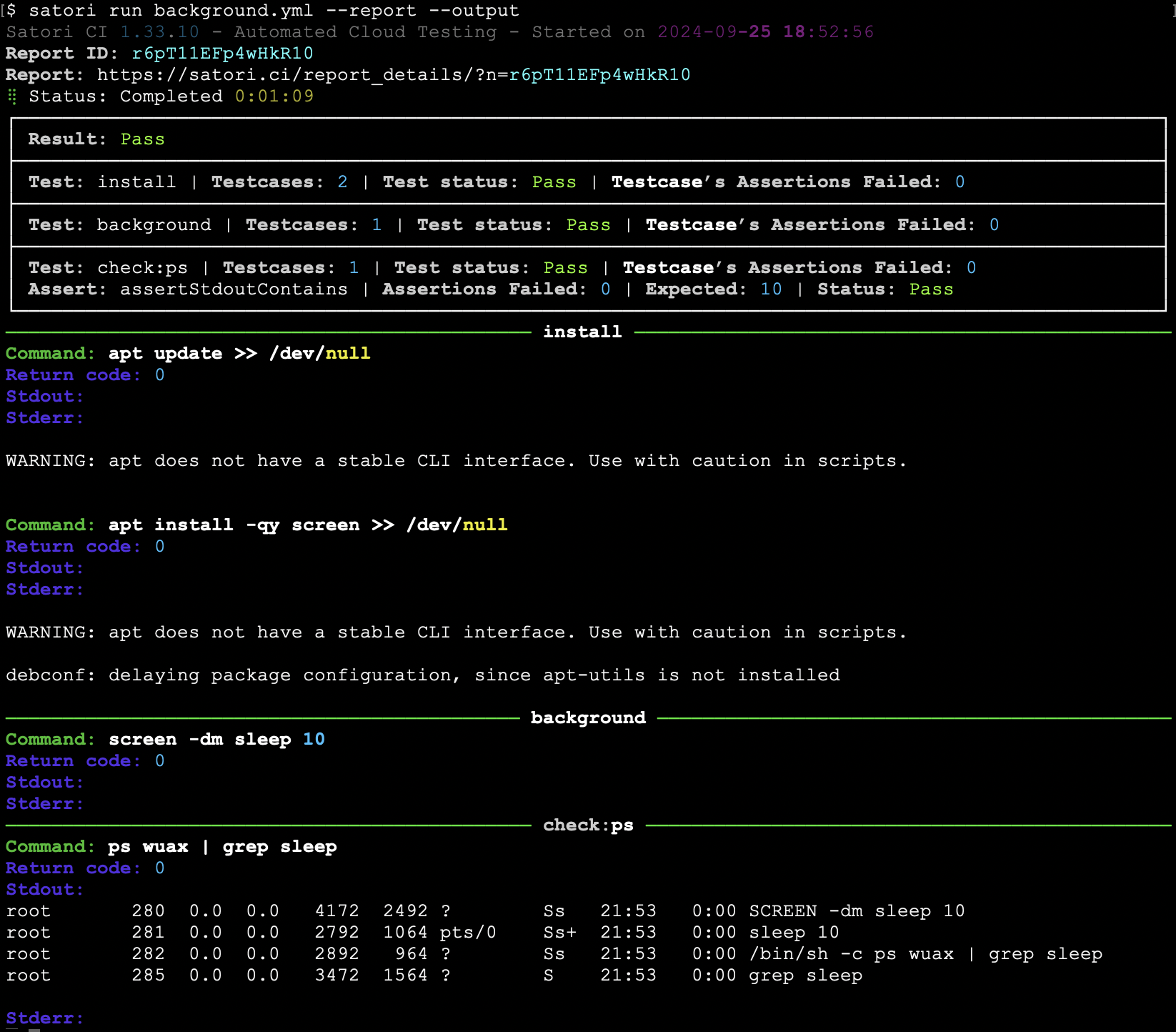
The command screen -dm is used to start a new detached screen session in the background. This is useful for running commands or scripts in the background and continue executing additional commands to test the background service.
Advanced Run Command Options
The satori run command provides extensive options for controlling execution behavior, environment configuration, and output handling.
File and Data Management
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
-i, --include FILE | Include additional files in the execution context (repeatable) | satori run ./ -i config.yaml -i data.json |
-df, --data-file KEY=PATH | Load variable values from a file (repeatable) | satori run ./ -df PAYLOAD=/path/to/data.txt |
--clone REPORT_ID | Clone settings from an existing report | satori run ./ --clone AOQxDWDkXpZp |
Execution Environment
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--cpu COUNT | Set CPU cores (256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096, 8192, 16384) | satori run ./ --cpu 2048 |
--memory MB | Set memory allocation in MB (512, 1024, 2048, 3072, 4096, 5120, 6144, 7168, 8192, 9216, 10240, 11264, 12288, 13312, 14336, 15360, 16384, 17408, 18432, 19456, 20480, 21504, 22528, 23552, 24576, 25600, 26624, 27648, 28672, 29696, 30720, 32768, 36864, 40960, 45056, 49152, 53248, 57344, 61440, 65536, 73728, 81920, 90112, 98304, 106496, 114688, 122880) | satori run ./ --memory 2048 |
--storage GB | Set storage allocation in GB | satori run ./ --storage 50 |
--os {windows|linux} | Select operating system | satori run ./ --os linux |
--image IMAGE_NAME | Specify custom Docker image | satori run ./ --image ubuntu:22.04 |
Scheduling and Monitoring
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--rate EXPRESSION | Create monitor with rate-based scheduling | satori run ./ --rate "every 5 minutes" |
--cron EXPRESSION | Create monitor with cron schedule | satori run ./ --cron "0 * * * *" |
--count NUMBER | Number of executions for monitor | satori run ./ --rate "every 5 minutes" --count 10 |
Note: --rate and --cron are mutually exclusive. Use one or the other to create scheduled monitors.
Repository Scanning
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--repo URL | Specify repository to scan | satori run --repo github.com/user/repo -d PARAM=value |
Output and Report Control
| Flag | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--format {plain|md} | Set output format (plain text or Markdown) | satori run ./ --sync --output --format md |
--redacted PARAM | Mark parameters as redacted in logs (repeatable) | satori run ./ --redacted API_KEY --redacted PASSWORD |
--save-report {true|false|PATH} | Save report to file or default location | satori run ./ --save-report true |
--save-output {true|false|PATH} | Save command output to file | satori run ./ --save-output ./output.log |
Complete Example with Multiple Options
satori run ./ \
-d API_KEY=secret \
-i config.yaml \
--cpu 4 \
--memory 2048 \
--timeout 600 \
--sync \
--report \
--output \
--format md \
--redacted API_KEY \
--save-report trueThis command runs the current directory's playbook with:
- Secret parameter
API_KEY - Additional config file included
- 4 CPU cores and 2GB memory
- 10-minute timeout
- Synchronous execution with report and output
- Markdown-formatted output
- API_KEY redacted in logs
- Report saved to file
